Technology
What is EJOSA Template?
- EJOSA Template offers easy to use templates and is a good starting point for your J2EE development based on Enhydra and JOnAS application structure.
- EJOSA Template provides a collection of Open Source components which are bundled together and already pre-configured, so there is no need to download all the components separately (see ejosa/ext-libs/readme-external-libs.txt for a list of included components). Just unpack the file and you have everything you need to start your J2EE development.
- EJOSA Template defines an easy to understand structure to be followed by the development of J2EE applications.
- EJOSA Template does not use IDE, wizards or assistants. This means you need to understand the whole process before you can develop your own J2EE application. On the other hand you have the freedom to choose your own IDE.
- EJOSA Template can be used to make a prototype fast and easily without having to throw the prototype result for continuing the project. This means projects use EJOSA Template can scale.
- EJOSA Template combines Model Driven Architecture (MDA) and Sourcecode Centric Development (SCD) model. It allows you to integrate both models in one environment to get the best of both worlds. It is very important to integrate the modelling part of the components directly into the developer's compile, run and test cycle.
These are some aspects from the J2EE-Technology used by the EJOSA-Template model:
EJOSA Template uses best practices from Model Driven Architecture concept from Object Management Group (OMG) which consist following elements:
- Application of available Reference Models.
- Application of Product-Line Software Engineering which separate Domain Engineering and Application Engineering.
- Application of Architecture and Pattern-based Techniques like using Common J2EE design patterns. EJOSA Template only uses some of the J2EE design patterns which are a must and does not try to use all of them. This keeps EJOSA Template simple.
- Application of Component-based Software Engineering
which consists of following techniques:
- Object-oriented and Extended Object-oriented Programming delivered by general purpose programming languages like using annotations and metadata,
- Generative Programming like using templates and generators,
- Programming using Frameworks,
- Aspect-oriented Programming and
- Business Rules Programming.
- Exeperiences taken from development of OpenUSS (http://openuss.sourceforge.net) and other applications.
Use of EJOSA in different information systems
Here is a typical use of EJOSA as your technical infrastructure:
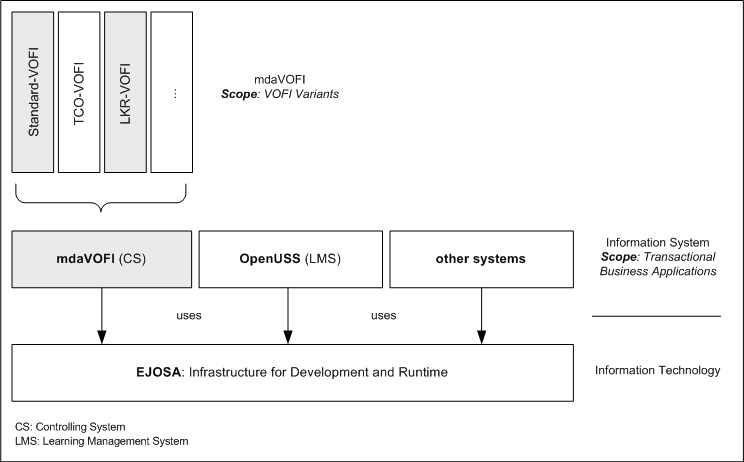
EJOSA can be used to create transactional business applications
(OpenUSS, mdaVOFI, etc. please see references).
For this purpose it uses AndroMDA general Model-Text/Code cartridges
(transformation definitions) which are using following language elements
e.g. <<Service>>, <<Entity>> and <<Identifier>>,
for building J2EE transactional applications. This is the scope of EJOSA
application variants.
Further you can build your own variants by defining your own application scope. An example for this purpose is the product family mdaVOFI which may consist many of VOFI variants (end products). These variants serve as the scope of mdaVOFI. In mdaVOFI you also have a VOFI language which is using following language elements e.g. <<VoofiVofi>>, <<VoofiPeriod>> and <<VoofiPayment>>. To be able to have an executable code you need to transform the VOFI language into a general transactional business application language based on the language elements described by AndroMDA (see above). To implement this, EJOSA uses Model-Model cartriges (transformation defiinitions) which is based on MTL and/or ATL.